This week in AI brings groundbreaking advancements, from real-time video game simulations to powerful image editing tools and agile robotics. Join us as we explore the latest innovations that are reshaping technology and our interaction with it.
Introduction to AI Developments
Artificial Intelligence continues to evolve at an astonishing pace. Recent advancements have opened new avenues in gaming, image editing, and animation. This week, we delve into some of the most remarkable developments that showcase the potential of AI.
Realtime Counter Strike Simulation
One of the standout innovations is Microsoft's Diamond, a groundbreaking AI that creates playable simulations of Counter Strike: Global Offensive. What sets Diamond apart is its ability to run on a consumer-grade NVIDIA RTX 3090, making it accessible to a wider audience.
Diamond utilizes a diffusion-based model, similar to those used in leading image and video generators. This model predicts the next frame by analyzing previous actions and gameplay data. Remarkably, it was trained on only 87 hours of gameplay, significantly less than required for comparable AI systems.
Players can interact with the simulation using standard keyboard and mouse inputs, making the experience immersive. The open-source code available on GitHub allows enthusiasts to install and run it locally, further democratizing access to advanced AI technology.
Google AI Image Editor: RF Inversion
Google's RF Inversion is a revolutionary image editing tool that transforms reference images based on user prompts. This AI-powered tool allows users to change elements in an image simply by describing what they want.
For instance, if a user inputs a reference image of a flower and prompts it with "face of a boy," the AI preserves the flower's details while altering the face. This capability extends to various transformations, including changing animals, objects, and even styles.
The semantic editing feature of RF Inversion means users can edit images intuitively without complex inpainting or masking techniques. By understanding user prompts, RF Inversion streamlines the editing process, allowing for quick and effective modifications.

AnimateX: Animation for Non-Human Characters
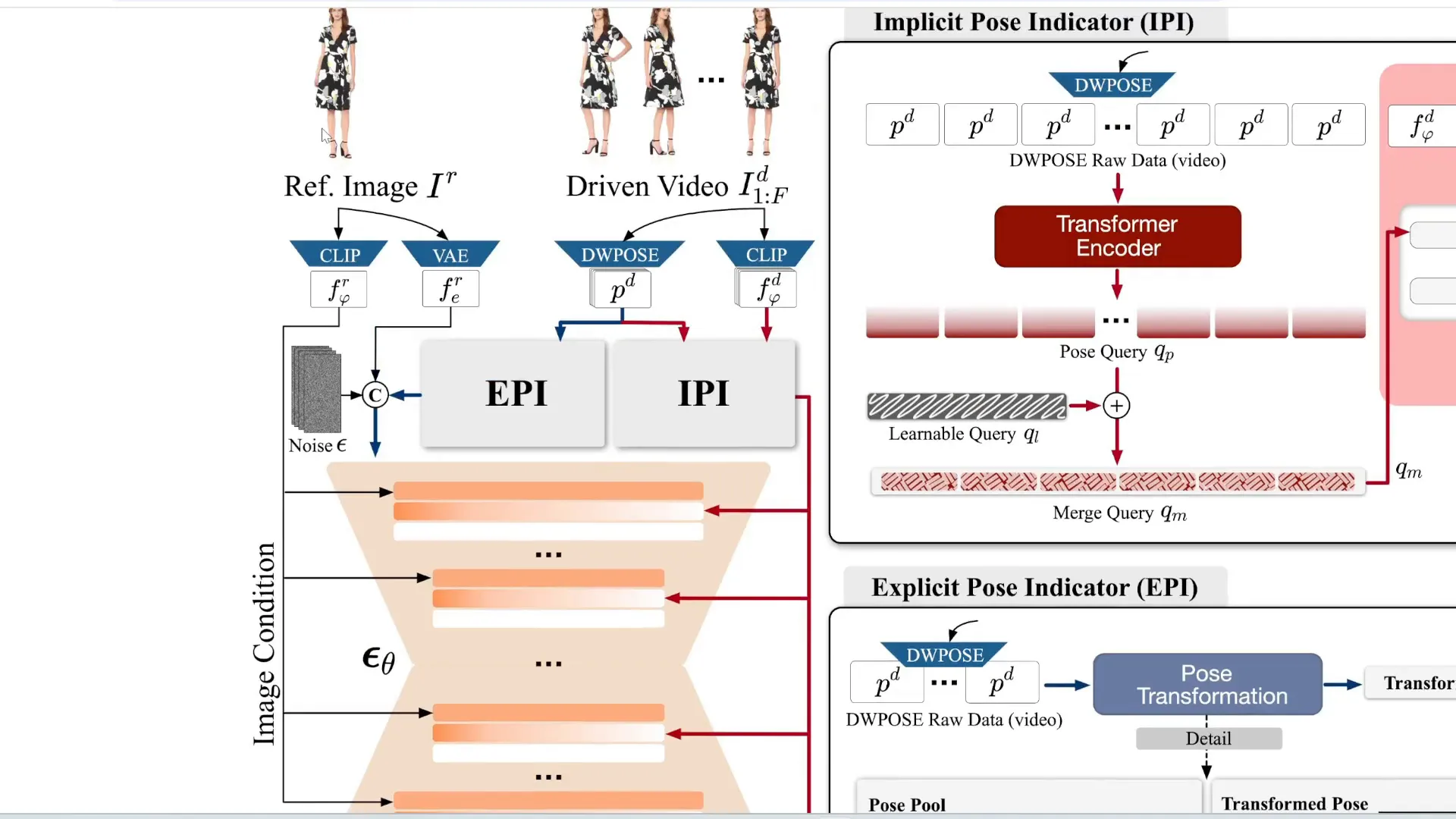
AnimateX is an innovative tool developed by Ant Group and Alibaba, designed to animate non-human characters, such as cartoons and animals. Unlike previous tools that struggled with non-human animations, AnimateX excels in this area, making it easier for creators to bring imaginative characters to life.
The process begins with a reference video that defines the desired movement. This video is converted into a pose video, which serves as a skeletal model for the character's movements. By combining this data with the input image of the character, AnimateX generates a final animated video using a diffusion model.
This tool is not only free and open source but also represents a significant leap in animation technology. With AnimateX, the need for traditional motion capture and complex modeling techniques may soon be a thing of the past, paving the way for more accessible animation creation.
Hallo2: Next-Gen Talking Head Generator
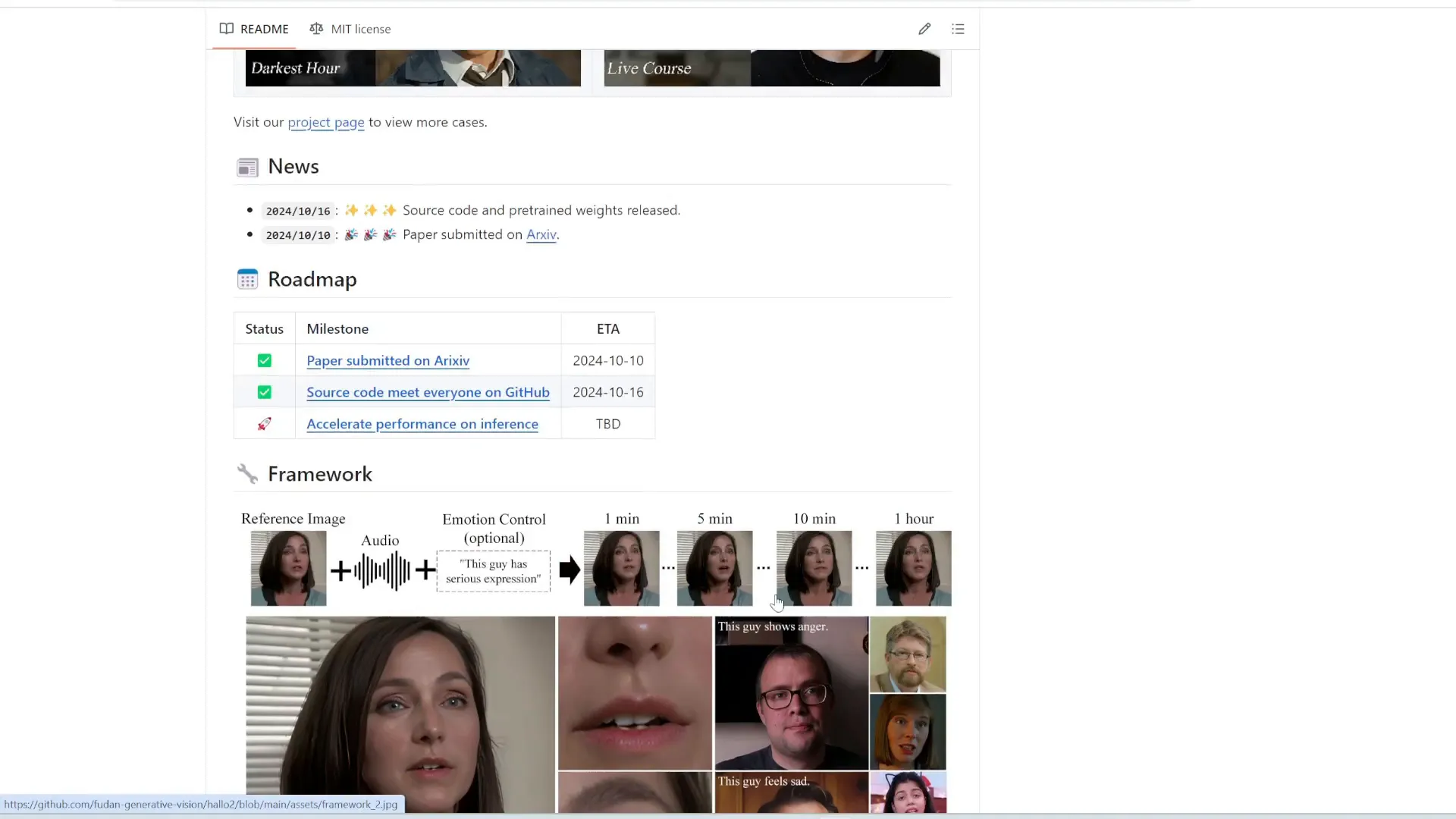
Hallo2 is the latest iteration of a free and open source talking head generator. This tool allows users to input any photo and audio, creating a realistic video of the face speaking the audio. The latest version supports up to 4K resolution, enhancing video quality significantly compared to its predecessor.
Hallo2 has expanded its capabilities, enabling the generation of longer videos, up to an hour. This advancement opens up new possibilities for content creators, educators, and marketers looking to produce engaging video content effortlessly.
With its improved resolution and extended duration, Hallo2 sets a new standard for talking head technologies, making it an invaluable resource in the realm of digital communication.

NotebookLM Updates: Smart Note-Taking
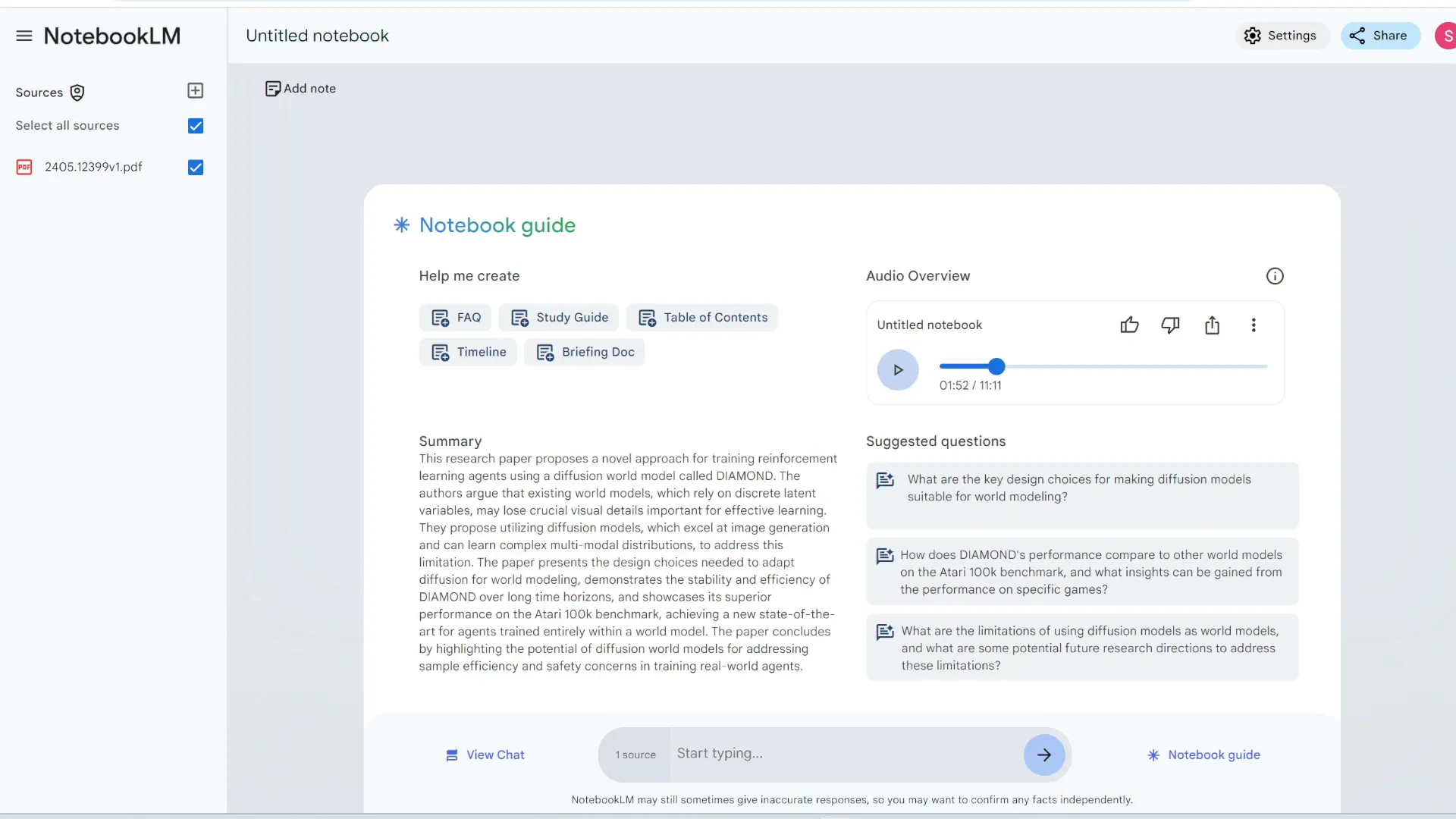
Google has unveiled exciting updates to NotebookLM, their powerful and free note-taking tool. This platform allows users to convert any document into an audio podcast, making information consumption more accessible.
After uploading a PDF, NotebookLM generates an audio overview, simulating a natural conversation between two hosts discussing the uploaded document. This feature is particularly beneficial for audio learners, enabling students to listen to lecture notes while multitasking.
New Features in Audio Overview
NotebookLM has introduced several new features to enhance the audio overview experience. Users can now customize the generated podcast by adjusting settings to focus on specific topics or alter the expertise level.
For instance, one could request a simplified explanation for a high school audience or a more technical discussion suited for PhD students. This level of customization allows for a tailored learning experience.
Background Listening Capability
Another significant addition is the ability to listen to NotebookLM in the background. Users can now browse other tabs while the audio continues to play, making it easier to engage with content without interruption.
This feature is particularly useful for those who may want to look up references or additional information while listening to the podcast. The seamless integration of multitasking capabilities enhances productivity and learning efficiency.
NotebookLM Business Version
For organizations, Google has announced a paid version called NotebookLM Business. This variant is designed for companies and universities, offering additional features tailored to professional and academic needs.
Interested parties can apply to the business pilot program for early access, indicating Google's commitment to expanding the tool's use in professional settings.
Unitree G1: The Athletic Robot
Unitree has showcased its G1 robot, an impressive feat of engineering known for its agility and athleticism. The G1 can jump an astounding 1.4 meters despite its height of only 1.32 meters, setting a record for humanoid robot jumps.
Unlike other humanoid robots that have garnered more media attention, such as Tesla's Optimus or the Figuero Robot, the G1 demonstrates superior jumping and running capabilities. This agility sets Unitree apart in the robotics landscape.
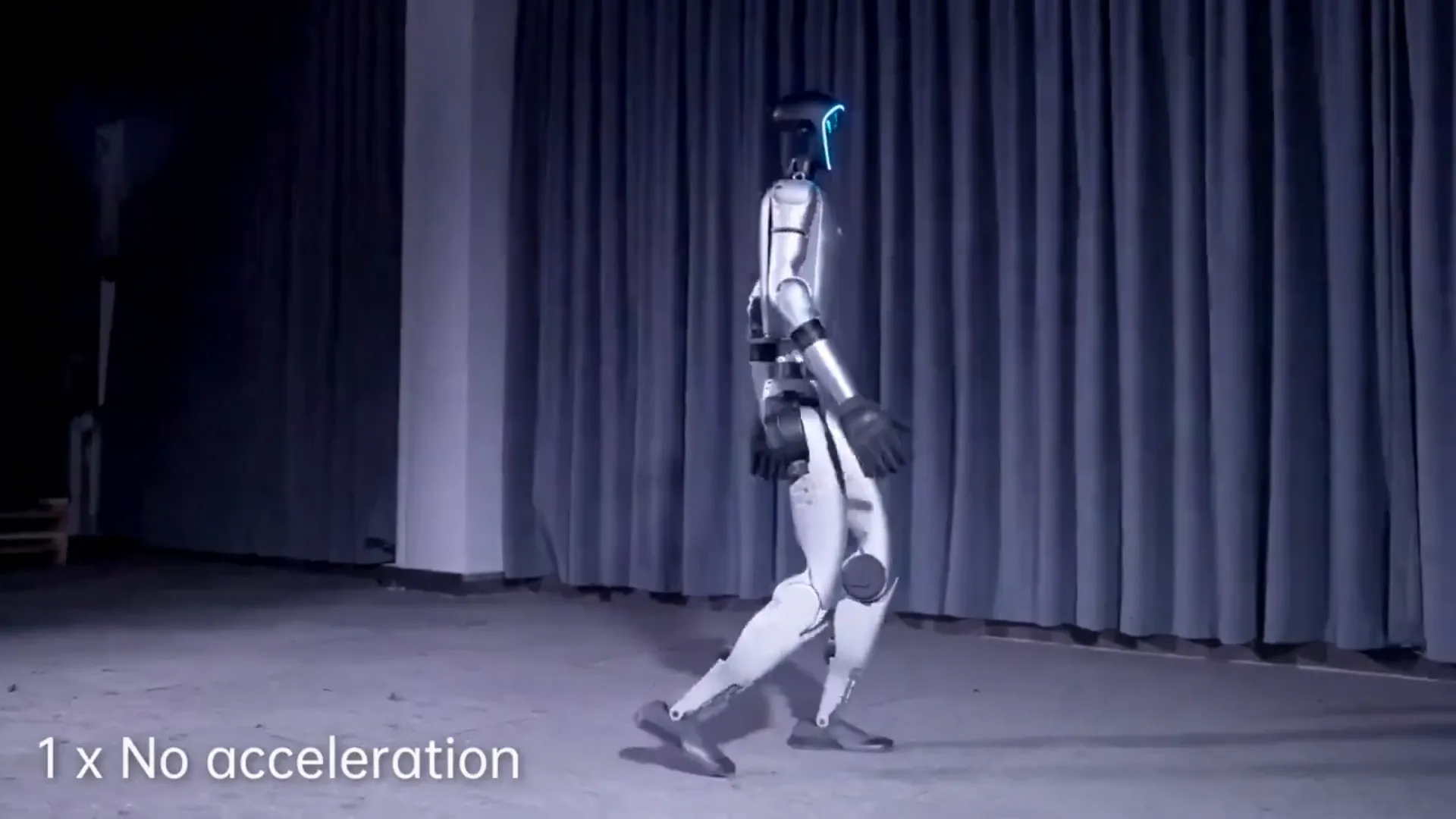

Affordability and Versatility
The G1 model is priced at a competitive $16,000, making it more accessible compared to similar robots. This affordability opens doors for various industries to explore robotic applications without prohibitive costs.
Additionally, Unitree's G1 is part of a broader lineup, including the H1, known as the fastest humanoid robot and the first fully electric robot to perform a backflip. These advancements highlight Unitree's dedication to pushing the boundaries of robotics.

Newton: AI Understanding Real-World Physics
Archetype AI has introduced Newton, an innovative AI model designed to interpret and understand the physical world using sensor data. Unlike traditional AI systems, Newton learns autonomously, without explicit instruction on the laws of physics.
By analyzing data from various sensors, including radars and cameras, Newton has made remarkable predictions, such as chaotic pendulum motions and citywide power consumption forecasts. These capabilities demonstrate its potential across numerous applications.
Real-Time Processing and Adaptability
Newton's ability to process data and make real-time predictions is crucial for practical applications in industries like energy and robotics. Furthermore, it can quickly adapt to new domains with minimal additional training, enhancing its utility in diverse environments.
This flexibility positions Newton as a revolutionary tool in AI, bridging the gap between traditional models and real-world applications, potentially leading to new discoveries in physics and engineering.

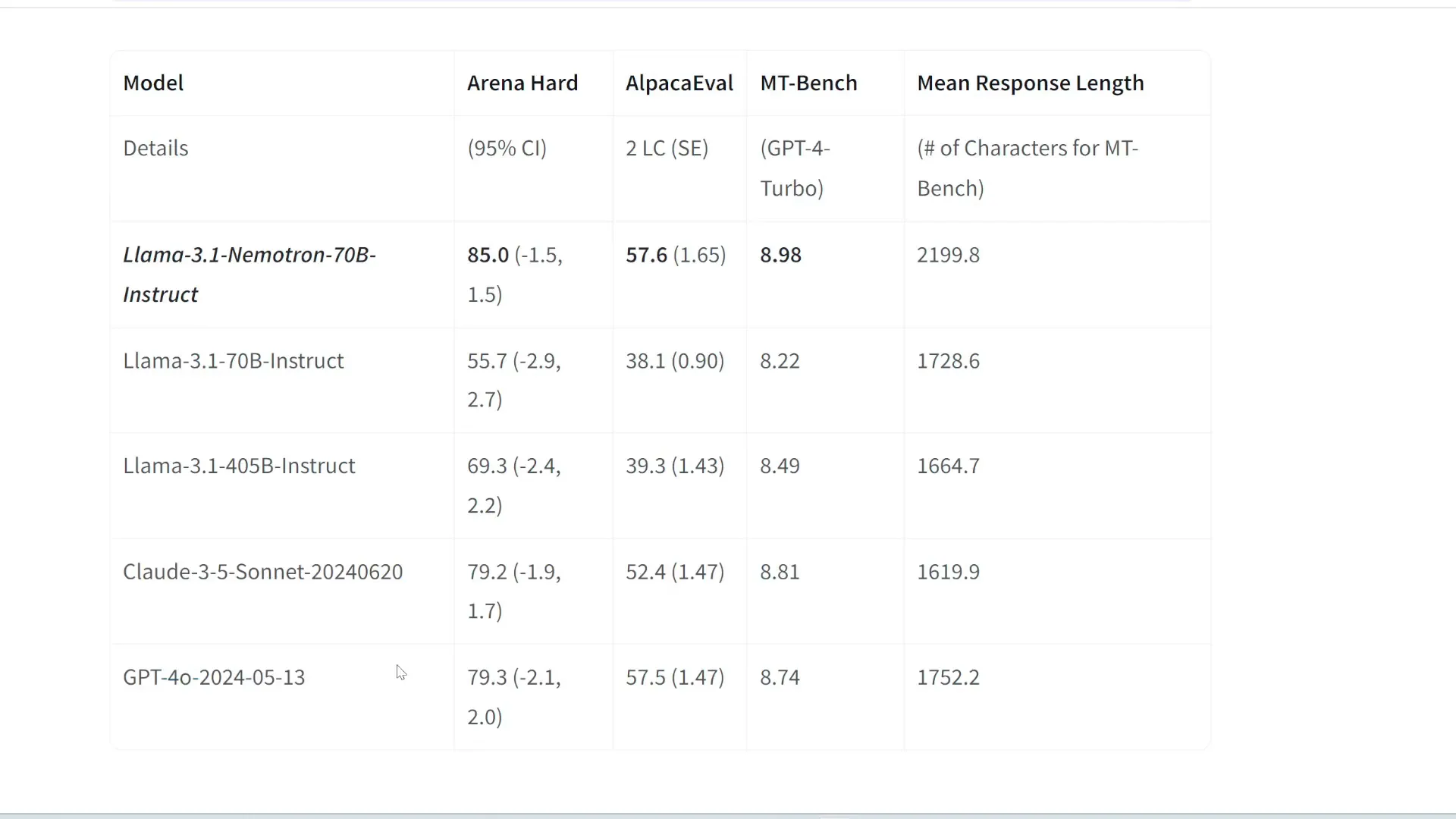
Nvidia's New Models: Llama 3.1 Nemotron
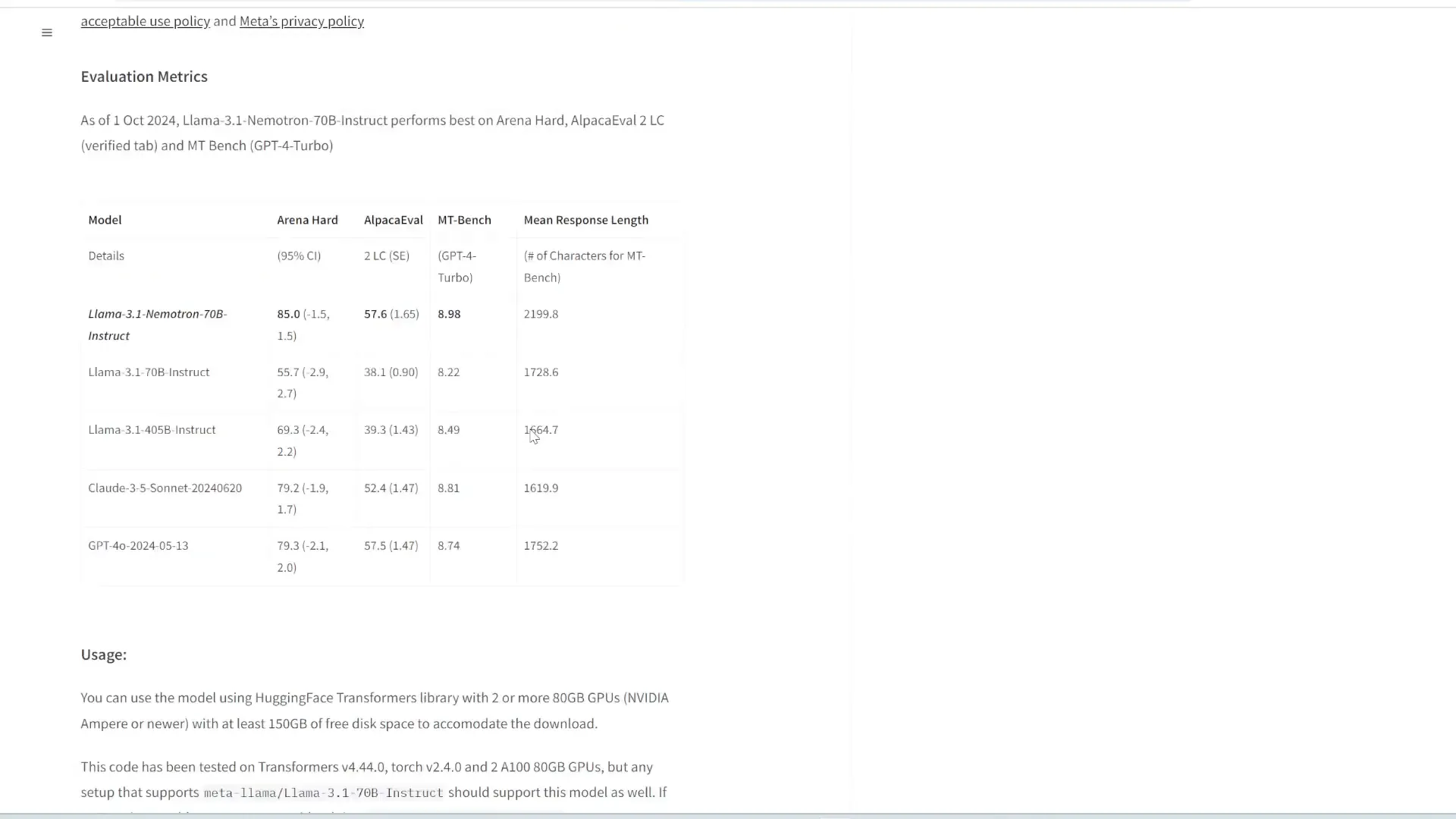
NVIDIA has launched the Llama 3.1 Nemotron, a 70 billion parameter model that showcases impressive performance in various benchmarks. Despite being smaller than other state-of-the-art models, Nemotron outperforms them in specific areas, such as instruction following and real-world applications.
The model achieves top scores in benchmarks like ArenaHard and Alpaca Eval, indicating its effectiveness in practical scenarios. This success demonstrates that smaller models can still deliver high-quality results without the need for excessive parameters.
Open Source Accessibility
One of the most exciting aspects of Nemotron is that NVIDIA has open-sourced the model and its training data. This move allows developers and researchers to download, run, and fine-tune the model locally, promoting innovation and collaboration within the AI community.
Accessibility to such advanced technology can lead to breakthroughs in various fields, as more individuals and organizations can experiment with and build upon NVIDIA's work.
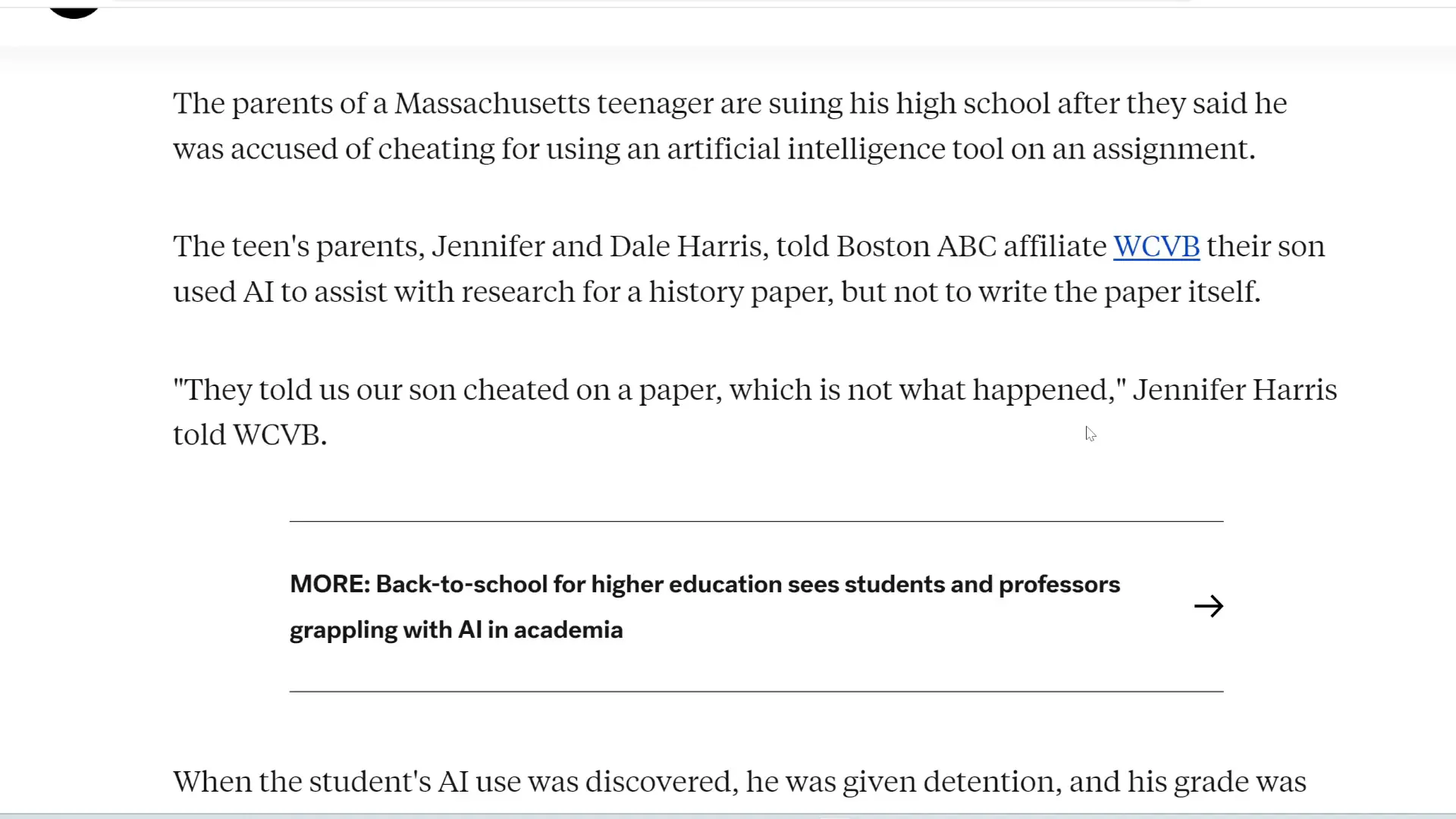
School Gets Sued Over AI Use
In a notable case, a high school student found himself in legal trouble after using AI tools for homework assistance. The school accused him of cheating, leading to severe penalties, including zeros on assignments and removal from the National Honor Society.
The student's parents are now suing the school district, arguing that the punishment was excessive and that the school's policies on AI usage were unclear. This situation raises significant questions about the role of AI in education and its implications for academic integrity.

Implications for Educational Policies
This case highlights the growing need for clear guidelines regarding AI usage in educational settings. As AI tools become more prevalent, schools must establish policies that reflect the changing landscape of learning and technology.
The outcome of this lawsuit could set important precedents for how educational institutions handle AI, potentially influencing future regulations and practices in schools nationwide.
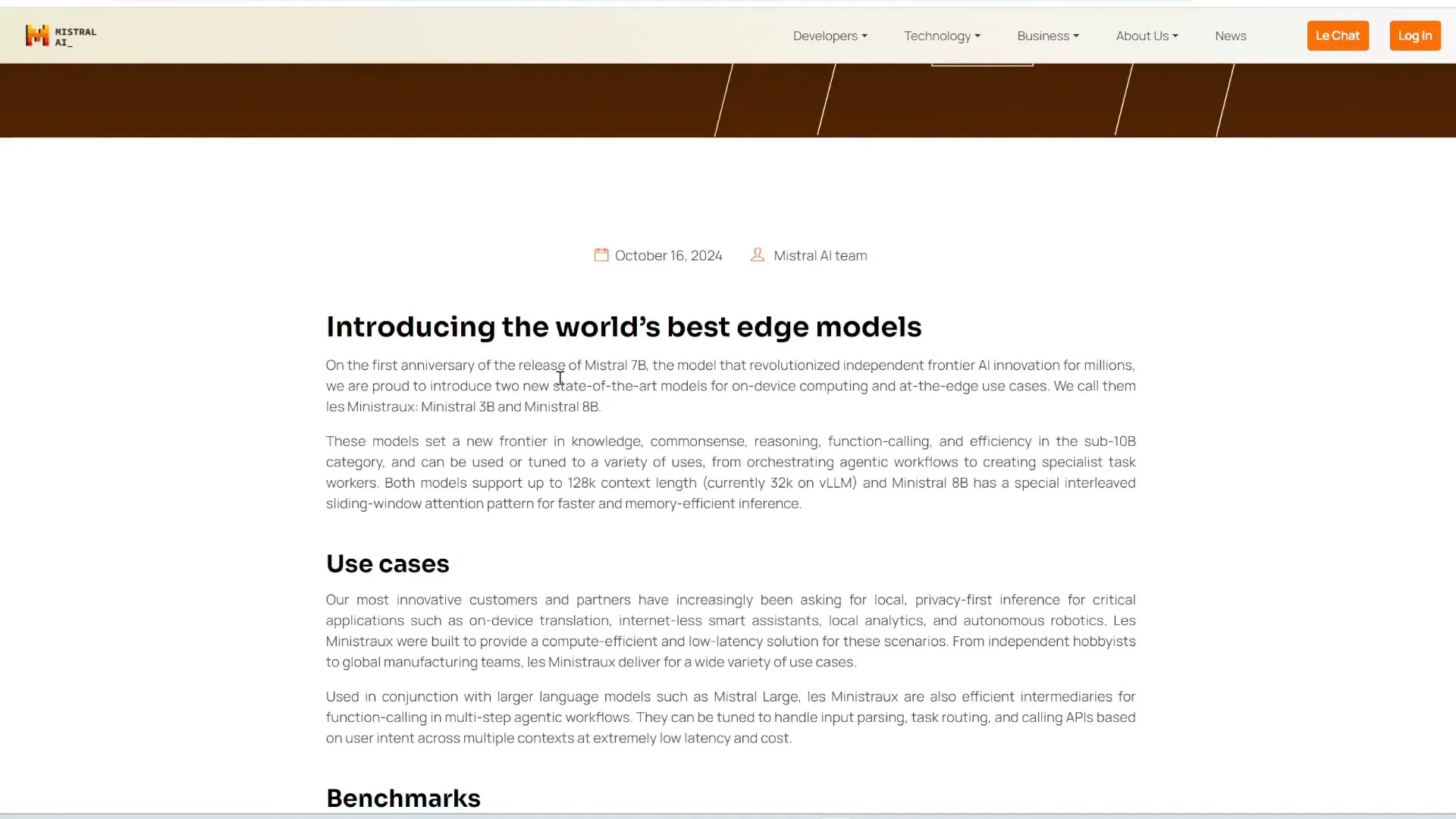
Mistral's Small Language Models for Edge Devices
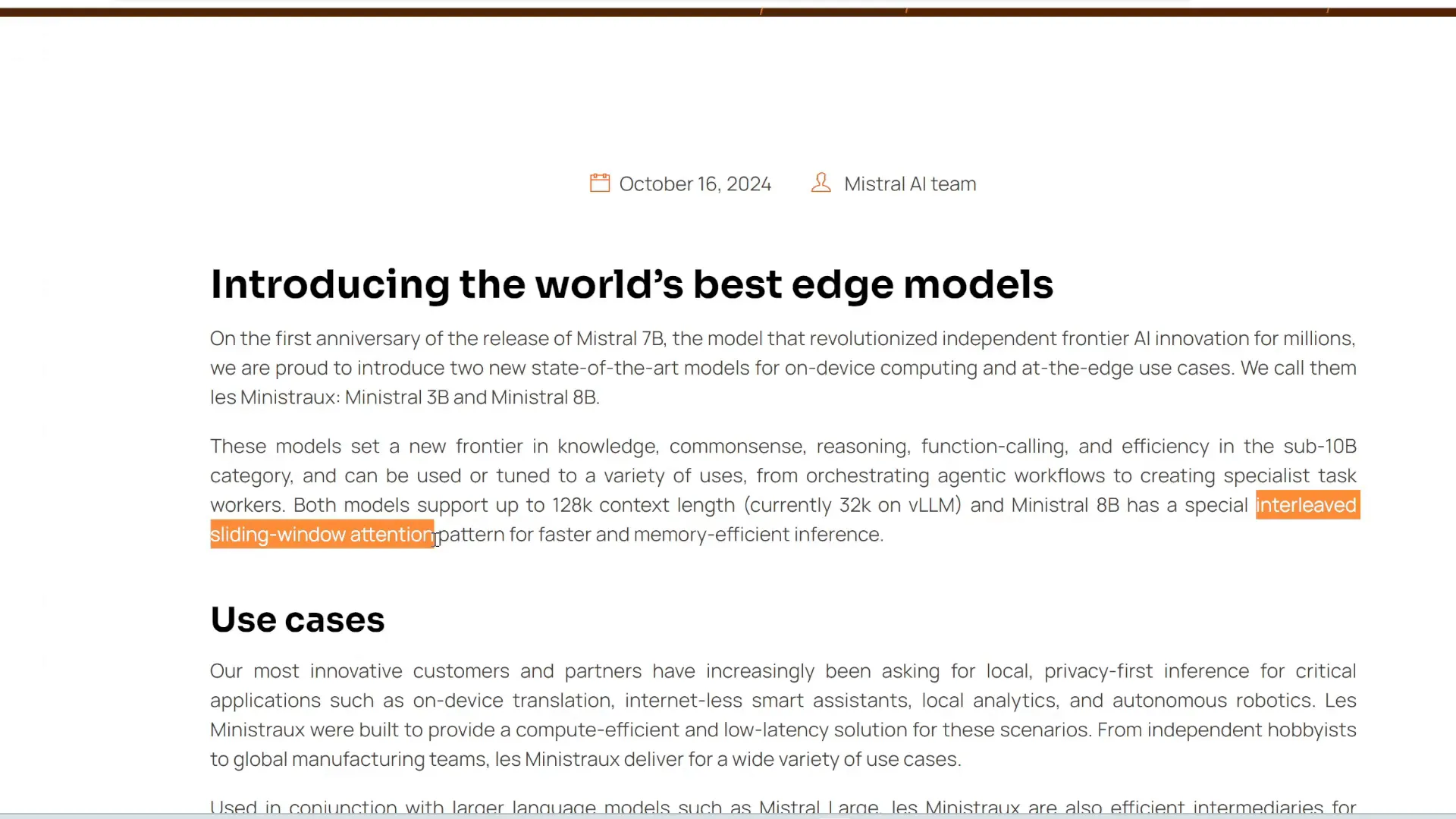
Mistral has introduced a new family of small language models, specifically the Mistral 3B and Mistral 8B. These models are notable for their efficiency and performance, particularly in resource-constrained environments such as smartphones and laptops.
The Mistral 8B model features an innovative interleaved sliding window attention mechanism, which significantly enhances memory efficiency. Despite their compact size, these models have shown superior performance compared to larger competitors like GEMMA and LLAMA on various benchmarks.
Performance Benchmarks
The Mistral 3B model has outperformed LLAMA 3.2 across all tested benchmarks, demonstrating its capability even with fewer parameters. Meanwhile, the Mistral 8B model also excels against LLAMA 3.1, except in the Human Eval benchmark, which highlights its versatility.
It's important to consider that self-reported benchmarks should be viewed with caution. Independent evaluations would provide a clearer picture of these models' standings in the AI community.
Implications for Edge Computing
The trend towards smaller, more efficient language models is paving the way for a future where AI functionalities such as translation and writing can be performed locally on devices. This means less reliance on cloud services, enhancing privacy and reducing latency.
In the coming year, we can expect an increase in devices equipped with these models, making advanced AI capabilities accessible to a broader audience.

YouTube's Dreamtrack: AI-Generated Music
YouTube has launched an exciting feature called Dreamtrack, designed to assist content creators in generating original music for their videos. This tool enables users to input prompts and generate instrumental tracks tailored for YouTube Shorts.

How to Use Dreamtrack
To create music using Dreamtrack, users simply tap the "add sound" option in the Shorts camera, select "create," and enter their desired prompt. They can also choose a music style before finalizing the creation process.
This feature is currently available to users in the United States, with plans for a global rollout soon. Dreamtrack represents a significant step forward in democratizing music creation, allowing creators to focus more on content while the AI handles the soundtrack.

Conclusion: The Rapid Evolution of AI
The advancements in AI technology this week reflect a broader trend towards efficiency, accessibility, and creativity. From Mistral's small language models that empower edge devices to YouTube's innovative Dreamtrack feature, these developments showcase the exciting potential of AI in everyday applications.
As we continue to witness these rapid changes, it is crucial for both creators and consumers to stay informed about the tools available to them. The landscape of AI is evolving quickly, and being aware of these innovations can greatly enhance productivity and creativity in various fields.

In conclusion, the future of AI holds immense promise, and as we embrace these technologies, we can expect even more groundbreaking advancements on the horizon. Stay tuned for more updates and insights into the world of AI.



0 Comments